Hermann Joseph Muller
From 1910 to 1915, Muller worked with Thomas Hunt Morgan. As we know Morgan’s experiment with mutant fruit flies proves the chromosomal theory of inheritance and Mendel’s work.
Muller introduced, induced mutation in genetics. He induced the mutation in sperm cells of drosophila or fruit fly. He did this with the help of X-rays which are called an X-ray-induced mutation.
He did his experiment between 1926/1927. He got a Nobel prize in 1946 for his excellent work.
Muller’s experiment opened a new door for scientists with his induced mutation.
Now, what is induced mutation?
Mutation can be natural or can be artificial in the gene of chromosomes. An example of natural mutation can be seen in fruit flies which have white eye color. While the mutation that can be introduced by man is called an induced mutation.
 |
| Induced Mutation |
Experiment.
- Muller’s experiment was started in 1926.
- Muller used fruit flies for his experiment.
- He exposed this fruit fly in front of X-rays.
- He just wants to know whether can mutation occurs artificially or if it's just always natural.
- He knows the genetic maker of the fruit fly.
Now, what is meant by genetic maker?
A genetic marker is the specific sequence of DNA at a known location on chromosomes. This genetic maker was present on X chromosomes in the male fruit fly, in the case of muller’s experiment.
 |
| Genetic maker |
It results in the shortening and thinning of bristles and this character was an X-linked chromosome of the male fruit fly.
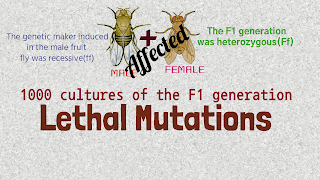
- After the exposure to X-rays, he mated this male fruit fly with a female fruit fly.
- The F1 generation was heterozygous.
- He also observed that the genetic maker induced in the male fruit fly was recessive.
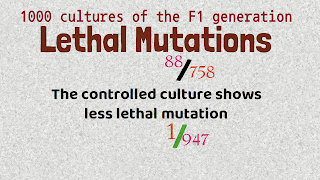
- Muller made about 1000 cultures of the F1 generation, in which the parents were affected.
- He observed lethal mutations in the affected parents.
Now, what is lethal mutation?
The lethal mutation is the type of mutation that causes the death of offspring before they are born.
- Muller observed 88 lethal mutations out of 758 cultures, which he treated with X-rays.
- While the controlled culture shows less lethal mutation. It was about only one lethal mutation out of 947 cultures of fruit flies.
 |
| Lethal mutation |
Conclusion.
- Muller concluded from his experiment that X-rays cause lethal mutation in the offspring of fruit flies.
- He also observed this lethal mutation in both male and female fruit flies. This shows that both male and female organisms of fruit flies are vulnerable to cause-induced mutation.
- He explains the term induced mutation very well and shows that X-rays can cause mutation.
- Muller warns others with his experiment that high-energy radiations or X-rays can cause negative effects on living cells, especially on germ cells.
- He advised others to be careful while dealing with these radiations.
- He highlighted the positive and negative effects of high-energy radiations or X-rays.

.png)




.png)
.png)
.png)
%C2%A0.png)
.png)
.png)


.png)

0 Comments