Algae
The study of algae is called "Phycology" It is a Greek word for the study of algae, which is the combination of two words Phykos and logos
- Phykos mean the seaweeds
- Logos means to discuss
Algae are more commonly called water mosses or seaweeds. The word "algae" has its origin in Latin, which stands for "seaweed".
The most common definition of algae is:
Chlorophyll-bearing aquatic organisms which are thalloid, range in organization from unicellular to multicellular and aquatic in distribution.
- Chlorophyll bearing means that they have chlorophyll in their cell structure
- Aquatic means they are found in water
- Thalloid means they lack true tissues like stem, leaf, root
- Maybe a single cell or group of cells like plants
They perform photosynthesis and are regarded as the main primary producers in the biosphere, especially in the oceans.
The cell structure of algae:
The algae may be eukaryotic or prokaryotic. A general cell of algae contains the following organelles;
- Cell wall
- Flagella
- Cell membrane
- Eyespot
- Cytoplasm
- Mitochondria
- Contractile vacuole
- Nucleus
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Reserve materials
- Chloroplast
- Paranoid
· And some starch molecules
Reproduction in Algae
Algae can be reproduced in different ways. Prokaryotic algae reproduce mainly by budding. Budding is a process in which an outgrowth develops from the cell and develops into a new cell.
Eukaryotic algae can have the types of reproduction like:
- Vegetative reproduction
- Asexual reproduction
- Sexual reproduction
Vegetative reproduction or fragmentation.
- It is the most common and simple type of reproduction in which any part of the body can reproduce.
- In this type of reproduction, Any part breaks and divides, and there is no formation of specialized structures (cells or organs).
- Sometimes, vegetative reproduction or fragmentation is not considered the type of reproduction because it occurs accidentally.
Asexual reproduction:
In asexual reproduction, spores are produced. Spores can form a new algal body, and spores can tolerate harsh or unfavorable conditions. Spores may be motile or non motile,
Sexual reproduction:
- Sexual reproduction is the fusion of gametes,
- One gamete from the male sex organ is called antheridium, which is usually tiny and motile.
- The other gamete comes from the female part known as archegonium, which is mostly large and non-motile.
- If the Male and female gametes are formed on the same thallus then it is called monoecious algae
- If the Male and female gametes are created on different thalli then it is called dioecious algae.
Sexual reproduction has the following types:
- Isogamous
- Conjugation
- Anisogamous
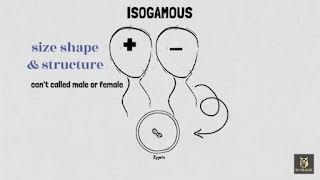
Isogamous
- This is the most primitive type of sexual reproduction.
- In this type, both males and female gametes are of the same size, shape, and structure.
- Because of the same size and structure, we are unable to differentiate them, so we can't be called male or female gametes.
- Because of this reason, we called them as plus (+) or minus (-) gametes.
- Both gametes fuse and form a zygote.
Conjugation:
- Conjugation is another type of sexual reproduction in which two different organisms come close to each other and exchange their genetic materials through a tube called a sex pill.
- After the exchange of genetic materials, both organisms get separated from each other.
- In this type, one organism has an extra genetic material that is specified for the conjugation process.
- This organism is called the donor because it donates its genetic material.
- The second organism that receives this material is called a receiver because it receives it.
- The receiver organism then produces a new individual after cell division.
Anisogamous:
- Anisogamous is the fusion of gametes with different sizes, shapes, and structures.
- One is called the male gamete while the other is called the female gamete.
- The male gamete is usually small and motile
- The female gamete is large and non-motile
- The fusion of these two results in the formation of a zygote.












.png)
.png)

.png)
%C2%A0.png)
.png)

.png)
.png)


0 Comments